401k contributions on W2 play a crucial role in retirement planning for many individuals. It is important to understand how these contributions are reported on your W2 forms, as they can have an impact on your tax obligations and overall financial planning.
Here is a guide on where to find 401k contributions on W2.
Locating 401k Contributions on W2 Form

To accurately locate your 401k contributions on W2, follow these detailed instructions:
- Start by obtaining your W2 form from your employer.
- Look for the section labelled “Wages and Compensation” or “Income and Tax Summary.”
- Locate Box 12 within this section, which may contain alphanumeric codes representing different types of compensation.
- Identify the specific code “D,” which represents 401k contributions.
- Note the amount listed next to code “D” as your reported 401k contributions.
- Verify the accuracy of the reported amounts
What Is a W2 Form?
It is an IRS–reporting 401k Contributions form of the income you earned during the year and the taxes withheld from your paycheck. It also includes benefits such as:
- Dependent care assistance
- Health insurance
- Life insurance policy
- Flexible spending accounts
- 401k plan
- Adoption assistance
- FSAs (Flexible Saving Accounts)
- HSAs (Health Savings Accounts)
W2 Form PDF
It is a crucial document for filing your income tax return.
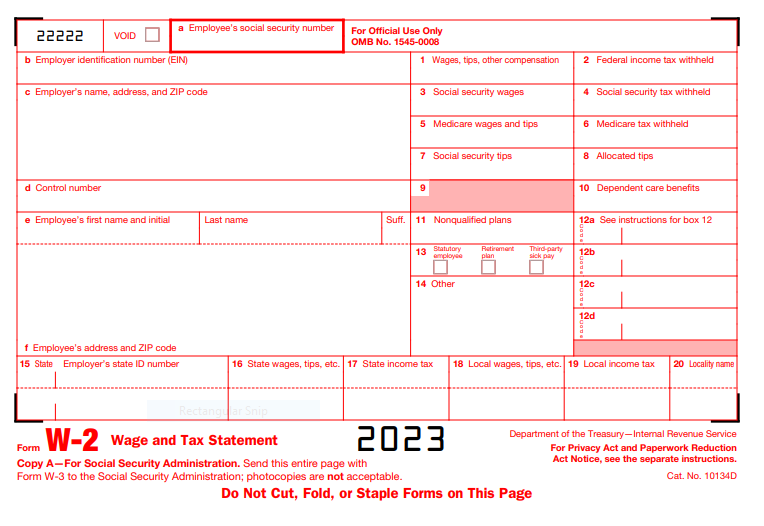
Understanding W2 Forms
A W2 form, also known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is a document that employers provide to their employees at the end of the tax year. It summarizes the income earned by the employee and the taxes withheld by the employer. Understanding the key components of a W2 form will help you navigate through the document and locate your 401k contributions effectively.
When are W-2 Forms Due?
W-2 forms are due no later than January 31st, following the close of the calendar year. Your employer must file W2 forms with the IRS and SSA by January 31st.
However, employers may request a 30-day extension by filling out Form 8809 and then sending a letter via fax to:
Internal Revenue Service Technical Services Operation
Attn: Extension of Time Coordinator
Fax: 877-477-0572 (International Fax: 304-579-4105).
The letter should include:
- Employers’ EIN
- Address and name
- Extension request statement
- Reasons for delay
- Signature
Even with the extension, they must provide employees with W2 forms by 31st, January. Unless they apply for 15-days extension to provide W2s after the due date,
Key Components of a W2 Form
A W2 form consists of several key components, including:
1. Employee Information
This section provides details about the employee. It includes:
- Employee’s name
- Social Security number
- Address
2. Employer Information
This section contains information about the employer, including:
- Employer name
- Employer address
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
3. Income and Taxes Related to Your Benefits
The tax related to your benefits includes:
- Insurance plans
- Health savings accounts
- Retirement plans
- Dependent care benefits
Note that you’ll only find on your W2 form benefits that your employer offer.
4. Income and Taxes Related to Your Wages
This section provides a breakdown of the employee’s income and taxes withheld. It includes information such as:
- Social Security
- Federal income taxes
- Actual income
- Medicare taxes
5. Income and Tax-related to state and local returns
The taxes related to your state and local returns include:
- Income and tax withholding( Home and work state)
- Local tax information
- Payment information such as tuitions unions dues, charities, and sick leaves
Importance of Reviewing W2 Forms for Accuracy
Reviewing your 401k contributions on W2 forms accuracy is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Tax Filing: Ensuring the information on your W2 form is correct is essential for filing your taxes accurately and avoiding potential penalties or audits.
- Proper Documentation: Your W2 form serves as official documentation of your income and tax withholdings, which may be required for various purposes such as obtaining loans, applying for financial aid, or verifying income for government programs.
- Identifying Errors or Fraud: Reviewing your 401k contributions on W2 form allows you to identify any errors or discrepancies, such as incorrect income amounts or unauthorized deductions, which may indicate potential fraud or identity theft.
- Maximizing Tax Benefits: By verifying the accuracy of your W2 form, you can ensure that all eligible tax credits and deductions are properly reflected, potentially maximizing your tax benefits and reducing your overall tax liability.
- Resolving Issues Promptly: If you identify any errors on your 401k contributions on W2 form, reviewing it early gives you ample time to reach out to your employer or relevant authorities to rectify the discrepancies and avoid delays in filing your taxes or receiving refunds.
Reporting 401k Contributions on W2 Forms
Reporting your 401k contributions on the W2 form accurately is essential for proper tax filing. By understanding where to find the relevant section on your W2 form and verifying your 401k contribution amounts, you can ensure accurate reporting and maximize the benefits of your retirement savings plan.
Location of 401k Contributions on a W2 Form
To report your 401k contributions correctly, you need to locate the specific section on your W2 form. This information can be found in Box 12 with a label indicating the type of 401k plan.
Box Number and Label for Reporting 401k Contributions
When you locate Box 12 on your W2 form, you will find various codes used to identify different types of compensation. The specific code for reporting 401k contributions on W2 is usually “D.” Let’s explore various codes on Box 12:
Box 12 CODES
In Box 12, CODES A&B represent amounts tipped to employees.
In Box 12, you will find CODES D, E, F, G, S, AA, and BB, which represent the contributions deducted from your payroll for your employer’s qualified retirement plan:
- CODE D stands for contributions to a 401(k) Plan.
- CODE E signifies contributions to a 403(b) Plan.
- CODE F represents contributions to a Salary Reduction SEP Plan.
- CODE G indicates contributions to a 457(b) government plan.
- S denotes contributions to a SIMPLE-IRA Plan.
- CODE AA represents Roth 401(k) Contributions.
- CODE BB signifies Roth 403(b) Contributions.
- CODE EE represents Roth 457(b) Contributions. (Please note that these amounts include any “catch-up” contributions made based on your age.)
Code C, Box 12, you must report any group-term life insurance coverage provided by your employer exceeding $50,000.
CODE L, Box 12, covers reimbursements for business mileage exceeding 56.5 cents per mile, also included in Box 1 wages.
For CODES M&N, Box 12, if you retired with over $50,000 in group-term life insurance and terminated retirement, uncollected social security and Medicare taxes are reported here.
CODE P, Box 12, is used for reporting job-related moving expenses paid by your employer that are not taxable.
CODE W, Box 12, indicates HSA contributions made by both the employer and employee, excluding after-tax HSA contributions.
CODE Y, Box 12, reports current-year deferrals to a Section 409(a) non-qualified deferred compensation plan.
CODE DD, Box 12, provides the cost of employer-sponsored health coverage, encompassing both employer and employee shares for informational purposes.
Other boxes on W2 Form
BOX 1 contains your income like wages, bonuses, commissions, and tips. It also includes things like company car use, non-accountable expense reimbursements, and the cost of group term life insurance over $50,000.
BOX 1 adjusts for elective deferrals to retirement plans but not Roth contributions. It also accounts for pre-tax deductions for health insurance, flexible spending accounts, and HSA contributions. For pastors, it considers the designated “housing allowance.”
BOXES 2, 4, 6, 17, and 19 show the taxes withheld. These boxes may have figures from multiple states or local jurisdictions. Box 6 includes the new Medicare tax for wages over $200,000.
BOXES 3 and 5 report wages subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes. Box 3 has a limit, but Box 5 doesn’t. They include pre-tax contributions to retirement plans but exclude “S” Corporation health insurance premiums.
BOX 7 reveals tip income reported to your employer, which is also in Box 1.
BOX 10 shows pre-tax payroll withholdings for dependent care benefits.
BOX 11 discloses payments from non-qualified plans, reported in Box 1 wages.
In BOX 13, you should check this box if you were an “active participant” in your employer’s qualified retirement plan during the year, which includes pension plans, 401(k)s, 403(b)s, SIMPLE IRAs, and SEP Plans. However, do not check this box for a Section 457 government plan.
BOX 14 serves as a platform for employers to provide additional information that is not mandated by the IRS but can aid employees in their personal income tax preparations. Information of Box 14 include:
- Housing allowance for clergy
- “S” Corporation health insurance premiums (also included in Box 1 wages)
- After-tax health insurance premiums
- Union dues
- Uniform expenses
- After-tax HSA contributions
- Section 529 Plan Contributions
- Personal use of a company car (also reported in Boxes 1, 3, and 5)
- Any other information an employer wishes to convey to employees.
Also read: How to Rollover 401k contributions to Vanguard
Importance of Verifying 401k Contribution Amounts
Verifying the accuracy of your reported 401k contribution amounts is crucial. Here’s why:
- Tax Deductibility: Ensuring the correct contribution amount is reported on your 401k contributions on W2 form ensures that you receive any eligible tax deductions associated with your 401k contributions.
- Tax Compliance: Accurate reporting of your 401k contributions helps you comply with tax regulations and avoid potential penalties or audits.
- Retirement Planning: Verifying your 401k contribution amounts allows you to track your progress toward your retirement savings goals and make necessary adjustments if needed.
The Tax Advantages of 401k Contributions
401k contributions offer several tax advantages, including:
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Contributions and investment earnings grow tax-deferred within the 401k account until withdrawal.
- Lower Current Tax Liability: Pre-tax contributions reduce your taxable income in the year they are made, potentially lowering your current tax liability.
- Tax Savings: By contributing to a traditional 401k, you may save on taxes by deferring them to retirement when you may be in a lower tax bracket.
- Tax-Free Distributions: Roth 401k contributions, when qualified, can be withdrawn tax-free, providing tax-free income in retirement.
Impact of 401k Contributions on Taxable Income
401k contributions on W2 can have a significant impact on your taxable income. These include:
- Reduction in Taxable Income: Pre-tax contributions lower your taxable income for the year, which can potentially move you into a lower tax bracket and reduce your overall tax liability.
- Lower Tax Withholding: With lower taxable income, your employer may withhold fewer taxes from your paycheck throughout the year, giving you more take-home pay.
It is crucial to consult a tax professional for personalized advice regarding your specific financial situation. Tax laws can be complex, and individual circumstances vary.
A tax professional can help you understand the tax implications of your 401k contributions, provide guidance on optimizing your tax strategy, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Their expertise can help you make informed decisions and maximize the tax benefits associated with your 401k contributions.
Considerations for 401k Contributions
With 401k contributions, there are additional factors to consider beyond the basics. Here are some important considerations:
Employer Matching Contributions
Many employers offer a 401k matching program where they match a portion of the employee’s contributions. This is essentially free money that can significantly boost your retirement savings. Take advantage of this benefit by contributing enough to your 401k to maximize the employer match, as it provides an immediate return on your investment.
Vesting Schedules and Their Effect on 401k Contributions
Some employers may have vesting schedules that determine the portion of employer contributions you are entitled to if you leave the company before a certain period. Understanding your vesting schedule is crucial, as it affects the amount you’ll receive from employer contributions. Be sure to review your employer’s vesting policy to make informed decisions about your 401k contributions.
Traditional vs. Roth 401k Contributions and Their Tax Implications
Deciding between traditional and Roth 401k contributions is an important consideration. Traditional contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your current taxable income, but withdrawals in retirement are subject to income tax. They make Roth contributions with after-tax dollars, providing tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Consider your current and future tax situations to determine which option aligns best with your financial goals.
Benefits of Maximizing 401k Contributions for Retirement Planning
Maximizing your 401k contributions offers many benefits for retirement planning:
- Compound Growth: Contributing the maximum allowed amount allows your contributions to grow through compounding over time, potentially resulting in substantial retirement savings.
- Tax Advantages: Both traditional and Roth 401k contributions offer tax advantages, providing a tax-efficient way to save for retirement.
- Retirement Income: By maximizing your contributions, you increase the likelihood of having a significant and reliable income stream during retirement.
- Potential Employer Contributions: Maximizing your contributions can make you eligible for the full employer match, which can significantly enhance your retirement savings.
By considering these additional factors, you can make informed decisions about your 401k contributions and maximize the benefits for your retirement planning.
Common Issues and Resolutions with 401k Contributions on W2 Forms
While W2 forms provide valuable information about 401k contributions, there can be common issues that arise. Here are some common issues and their potential resolutions:
Issue 1: Missing or Incomplete 401k Contribution Information on W2 Forms
- Late Reporting: Employers may have delayed reporting of 401k contributions, resulting in the omission of information on the W2 form. Contact your employer to inquire about the status of the 401k contribution reporting and request an updated or corrected W2 form.
- Administrative Errors: Human errors or technical glitches during the payroll processing can lead to missing or incomplete 401k contribution information. Notify your employer’s payroll or HR department about the issue, providing them with the necessary details to rectify the error and issue an accurate W2 form.
Issue 2: Discrepancies Between Reported and Actual 401k Contributions
Steps to reconcile discrepancies:
- Review Documentation: Gather your 401k statements, pay stubs, and other relevant documentation that reflect your actual contributions. Compare them to the reported amounts on your W2 form.
- Contact Employer: If you identify discrepancies, contact your employer’s payroll or HR department to discuss the issue. Provide them with the documentation supporting your actual contributions and request a correction to the reported amounts.
- Request a Corrected W2 Form: If necessary, ask your employer to issue a corrected W2 form, known as a W2c, reflecting the accurate 401k contribution amounts.
Issue 3: Incorrectly Reported 401k Contributions Affecting Tax Calculations
Corrective measures to address tax-related issues:
- Review Tax Returns: If you discover that your tax return was filed with incorrect 401k contribution information, review your tax returns and identify the impact of the error on your tax calculations.
- File an Amended Return: If the incorrect reporting significantly affects your tax liability, consider filing an amended tax return, Form 1040X, to correct the error and ensure accurate tax calculations.
- Consult a Tax Professional: If you’re unsure about the appropriate steps to take or need guidance on the tax implications of the incorrect reporting, consult a tax professional. They can provide personalized advice and help you navigate the process of resolving tax-related issues.
By being proactive in addressing these common issues with 401k contributions on W2 forms, you can ensure accurate reporting, maintain tax compliance, and avoid potential penalties or audits.
Best Practices for Managing 401k Contributions and W2 Forms
To effectively manage your 401k contributions on W2 forms, it’s important to follow these best practices:
1. Regularly review and Retain Copies of Your W2 Forms
Review: Take the time to carefully review your W2 form each year. Ensure that all 401k contributions are accurately reported and match your records.
Retain Copies: Keep copies of your W2 forms in a secure location. These forms serve as documentation of your income, contributions, and tax withholdings and may be required for future reference, audits, or retirement planning.
2. Keep Your 401k Contributions Throughout the Year
Monitor Contributions: Stay proactive by monitoring your 401k contributions on W2 throughout the year. Keep track of the amounts you contribute, any employer matching contributions, and any changes to your contribution percentage.
Cross-Check: Regularly cross-check your records with the information provided on your pay stubs or online 401k account statements to ensure accuracy.
3. Communicate with Your Employer or HR Department Regarding Discrepancies
- Prompt Reporting: If you notice any discrepancies between your records and the information on your W2 form, promptly notify your employer or HR department.
- Provide Documentation: Support your concerns with relevant documentation, such as pay stubs or 401k statements, to help identify and rectify the discrepancies.
- Follow Up: Follow up with your employer or HR department to ensure that the discrepancies are addressed and resolved.
By implementing these best practices, you can effectively manage your 401k contributions and ensure accurate reporting on your W2 forms.
It’s important to maintain open communication with your employer or HR department and stay vigilant in reviewing and tracking your contributions throughout the year.
Taking these steps will help minimize errors, maximize the benefits of your 401k, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if my 401k contributions are not shown on my W2 form?
If your 401k contributions are not shown on your W2 form, you should contact your employer or the human resources department to address the issue. They can provide guidance on correcting the omission and ensuring your contributions are accurately reflected on your W2 form.
Are there any limits on 401k contributions reported on W2 forms?
Yes, there are limits on 401k contributions that can be reported on W2 forms. For the tax year 2023, the annual contribution limit for employees under the age of 50 is $19,500. Employees aged 50 and older can make catch-up contributions of an additional $6,500, for a total limit of $26,000.
How can I correct errors in the reported 401k contributions on my W2?
If you identify errors in the reported 401k contributions on your W2 form, you should notify your employer or the payroll department immediately. They will guide you through the process of correcting the errors and issuing a corrected W2 form, known as a W2c.
Do I need to report my 401k contributions when filing taxes?
No, you do not need to report your 401k contributions on W2 when filing your taxes. The contributions are already reflected on your W2 form, which is submitted to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) by your employer. However, it is essential to review the reported amounts for accuracy and ensure they align with your records.
Sources:
1. https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/fw2.pdf
2.https://www.irs.gov/instructions/iw2w3
