
What is Expense Ratio?
Expense Ratio is the percentage of a mutual fund’s or ETF’s assets used to cover the fund’s operating expenses. These expenses may include management fees, administrative fees, marketing and distribution expenses, and other costs incurred in managing the fund. It is deducted from the fund’s assets, reducing the overall returns an investor receives.
How to Calculate Expense Ratio
You can calculate an expense ratio using an expense ratio calculator by dividing a mutual fund’s or ETF’s total expenses by its average net assets. The result is expressed as a percentage, representing the portion of the fund’s assets used to cover the fund’s expenses.
The ER shows the costs incurred to operate a specific mutual fund or ETF, such as overhead and administrative expenses. Expenses for an expense ratio vary from one fund’s expense to another.
Some main components of an expense ratio include:
- Management fees
- Administrative fees
- Marketing and distribution expenses (12-1B distribution fees)
- Other operational expenses
Expense Ratio Formula
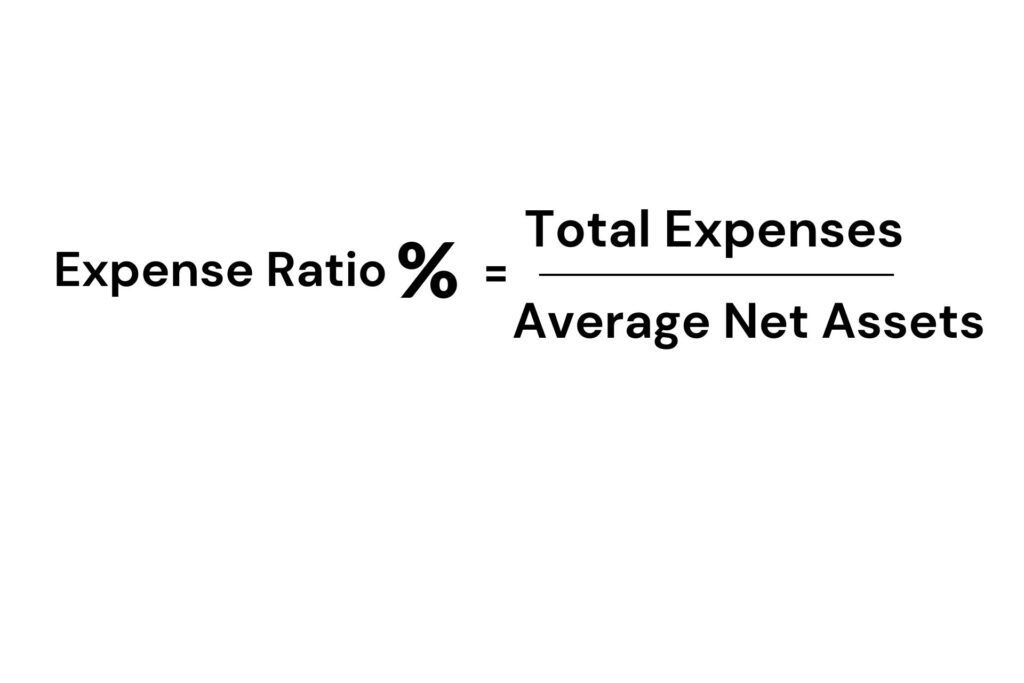
The average net assets represent the average value of the fund’s assets over a specific period, usually a year.
Understanding the Impact of Expense Ratio(ER) on Investment Returns
The Expense Ratio may seem like a small percentage, but it can significantly impact the overall returns investors receive from their investments.
Let’s say a mutual fund has an ER of 100%; 1% of the fund’s assets will cover the fund’s expenses, and the remaining 99% will be invested in securities.
In other words, if you invest $10,000 in a mutual fund with a 1% Expense Ratio, it will deduct $100 from your investment to cover the fund’s expenses.
It’s important to note that the ER is an annualized percentage, as it reflects the expenses incurred by the fund over a year, divided by the fund’s average net assets fund during that year. The Expense Ratio may vary annually, depending on the fund’s expenses and net assets.
Why is the Expense Ratio Important?
It is important when evaluating investment options because it directly affects investors’ expected returns.
A higher Expense Ratio indicates that a larger portion of the fund’s assets is used to cover expenses, resulting in lower net returns for investors.
A lower Expense Ratio indicates a smaller portion of the fund’s assets is used to cover expenses. Therefore, more assets are invested in securities, potentially resulting in higher net returns for investors.
What Is a Good Expense Ratio?
A good expense ratio depends on the investment fund’s style. For example; actively managed mutual funds have higher expense ratios compared to passively managed mutual funds.
Why? They require more hands-on management and monitoring by the fund manager.
A rule of thumb for evaluating a good expense ratio is as follows:
- For passively managed mutual funds, a good ER is around 0.20% (or even less in certain cases, i.e., 0.10%).
- In contrast, for actively managed funds, a good ER usually ranges around 0.5 to 1.0%.
Other variables to consider that determine the fund’s expense ratio are:
1. Fund size
The size of the fund can impact its Expense Ratio. Larger funds typically have economies of scale as they can spread their fixed costs over a larger asset base. The ER is often concerned with total net expenses, but people sometimes want to understand gross expenses versus net.
For example, the management fees of a company may include advertising and promotion expenses referred to on the mutual form line 12b-1, which include operating costs.
The fee cannot be more than 1%, where distribution allocates 0.75% and shareholder services 0.25%. Expenses such as redemption fees, loads, or contingent deferred sales charges are not included as the investor’s fund pays them directly.
2. Investment strategy
The investment strategy of a fund can also impact its ER. Funds requiring extensive research, analysis, and trading may have higher expenses than passively managed funds that track an index. Actively managed funds that invest in niche markets or complex securities may also have higher expenses than funds that invest in more traditional assets.
3. Asset class
In addition, the type of assets a fund invests in can also impact it. For example, funds that invest in international or emerging market securities may have higher expenses than those that invest in domestic securities due to the additional research, trading, and operational costs of investing in foreign markets.
4. Fund management company
Another factor is the company’s management funds. The company’s expenses and profit margins can also impact a fund’s ratio. Different fund management companies may have different fee structures and cost structures, which can result in variations in the Ratios for similar types of funds.
5. Share class
Many mutual funds offer different share classes, each with its own expense structure. For example, Class A shares may have front-end loads or sales charges, while Class B shares may have back-end loads or redemption fees.
These different share classes may have different Ratios. As an investor, you should review the expenses of each share class when evaluating funds.
Impacts of Expense Ratio on Investment Returns
Let’s take a closer look at how it can affect investment returns.
Lower returns
A higher ER means that a larger portion of the fund’s assets is used to cover expenses, leaving less money invested in securities. This can result in lower returns for investors, as the fund’s performance needs to overcome the drag of the expenses to generate positive returns.
Compounding effect
The impact of the Expense Ratio becomes more significant over time due to the compounding effect. As the fund’s expenses are deducted from the fund’s assets on an ongoing basis, the compounding effect can result in a substantial reduction in the overall returns that investors receive over the long term.
Comparative performance
In addition, it can also impact the comparative performance of a fund. A lower Expense Ratio can give a fund a competitive edge when comparing similar funds. That is by allowing more of the fund’s assets to be invested in securities, potentially leading to higher returns than funds with higher Expense Ratios.
Importance of cost management
Managing costs, including the Expense Ratio, is essential to overall investment performance. Investors should consider the Expense Ratio as part of their investment strategy and carefully evaluate the costs of the funds they are considering.
Key Takeaway
The expense Ratio is an important factor to consider when an investor is evaluating mutual funds and ETFs, as it directly impacts overall cost.
Understanding it and its impact on investment returns help investors make wise decisions and build a well-rounded investment portfolio.
It’s important for investors to review a fund’s Expense Ratio, along with other factors such as investment strategy, historical performance, risk profile, and fees.
It will help them to make the best investment choice based on their individual financial goals and risk tolerance.